UFC 4-023-03
25 January 2005
5-2.7
Vertical Ties.
All columns must be continuous through each beam-to-column connection.
All column splices must provide a design tie strength equal to the largest factored
vertical dead and live load reaction (from all load combinations used in the design)
applied to the column at any single floor level located between that column splice and
the next column splice down or the base of the column.
5-2.8
Columns with Deficient Vertical Tie Forces.
If it is not possible to provide the vertical required tie strength in any of the
columns, then apply the Alternate Path method for each deficient column. Remove
each deficient column from the structure, one at a time, and perform an AP analysis to
verify that the structure can bridge over the missing column. The specific details for AP
analysis of structural steel are provided next.
5-3
ALTERNATE PATH METHOD FOR STRUCTURAL STEEL.
The Alternate Path approach is used to verify that the structure can bridge
over removed elements. The general procedure provided in Section 3-2 must be
followed.
5-3.1
Acceptability Criteria for Structural Steel
The acceptability criteria are provided in Table 5-2; calculate the design
strengths per AISC LRFD 2003. The subsequent actions for the AP model after
violation of the acceptability criteria are detailed in the following sub-sections.
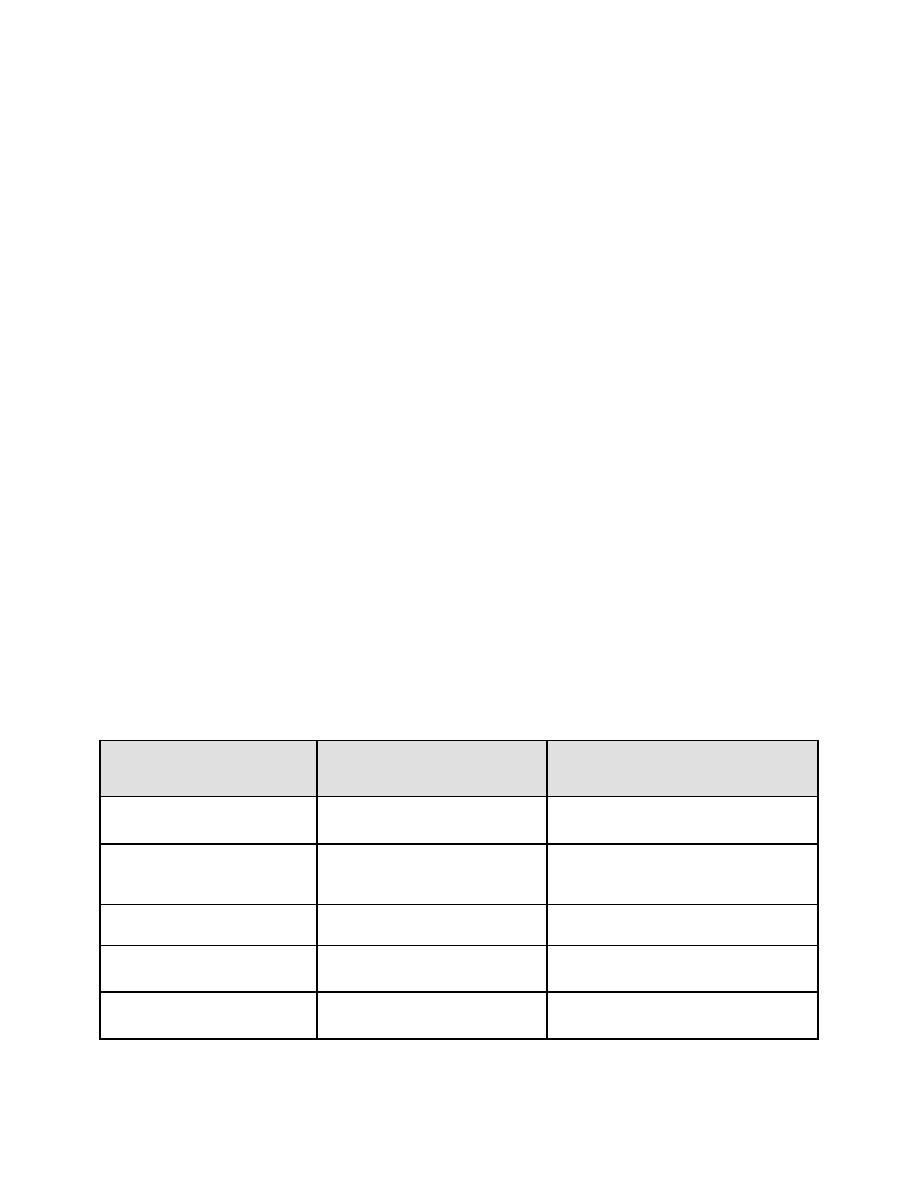
Table 5-2 Acceptability Criteria and Subsequent Action for Structural Steel
Subsequent Action for
Structural Behavior
Acceptability Criteria
Violation of Criteria
Φ MnA
Element Flexure
Section 5-3.1.1
Element Combined Axial
AISC LRFD 2003 Chapter
Section 5-3.1.2
H Interaction EquationsA
and Bending
Φ VnA
Element Shear
Section 5-3.1.3
Connection Design
Section 5-3.1.4
Connections
StrengthA
Deformation Limits,
Deformation
Section 5-3.2
defined in Table 5-3
5-5



 Previous Page
Previous Page
