UFC 3-570-06
JANUARY 31 2003
although the 100 mV polarization criterion can be used. For structures
which are bare, poorly coated, or have a deteriorated coating, the 100 mV
polarization criterion should be used.
7-3.2
Test Methods for the -0.85 ON Criterion. A single electrode potential
megaohms or higher). The voltmeter positive is connected to the structure under test
and the voltmeter negative is connected to the reference electrode to display the proper
polarity (for analog meters which only read in the positive direction, the leads must be
connected backwards to get an upscale deflection, and the negative value must be
inserted when recording the measurement). The -0.85 volts DC is measured to a
copper/copper sulfate reference electrode (half cell). Other types of reference
electrodes must be corrected to the copper/copper sulfate reference to use the -0.85
volt criterion.
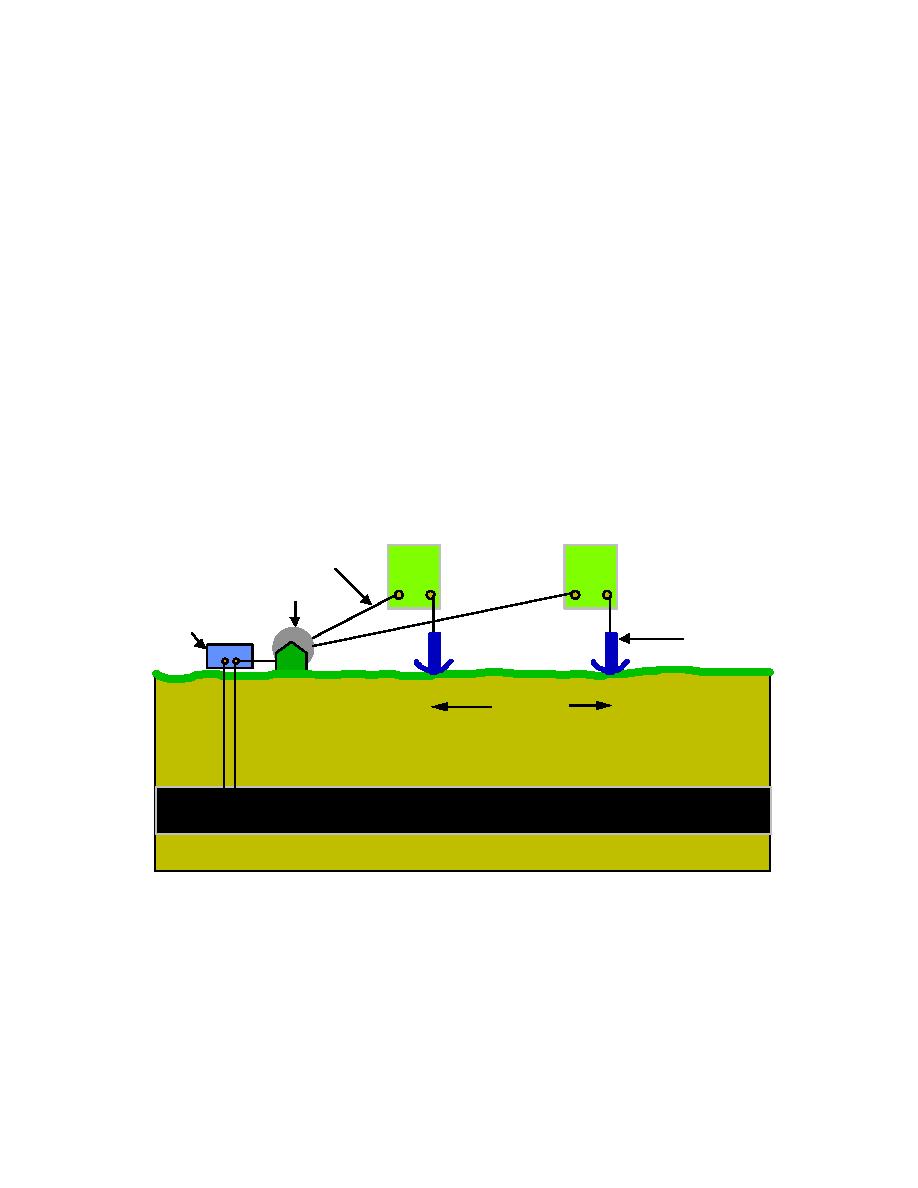
Figure 7-6. Single Electrode Potential Survey
V ol tm et e r
V oltm et e r
In sul a te d W ir e
+ -
+ -
W ire R eel
T e st St at io n
R e fe r e nc e
1
2
E le ct r od e
In te r v al
7-3.2.1
Since these potential readings are taken with the cathodic protection current
on, there are errors in the measurement which must be considered to obtain a valid
conclusion that adequate cathodic protection exists on the protected structure. Chapter
6 of this handbook and NACE International Recommended Practice (RP) 0169-92,
Section 6.2.2 for steel and cast iron piping, states that voltage drops other than those
across the structure-to-electrolyte boundary must be considered for valid interpretation
7-9



 Previous Page
Previous Page
