UFC 3-240-13FN
25 May 2005
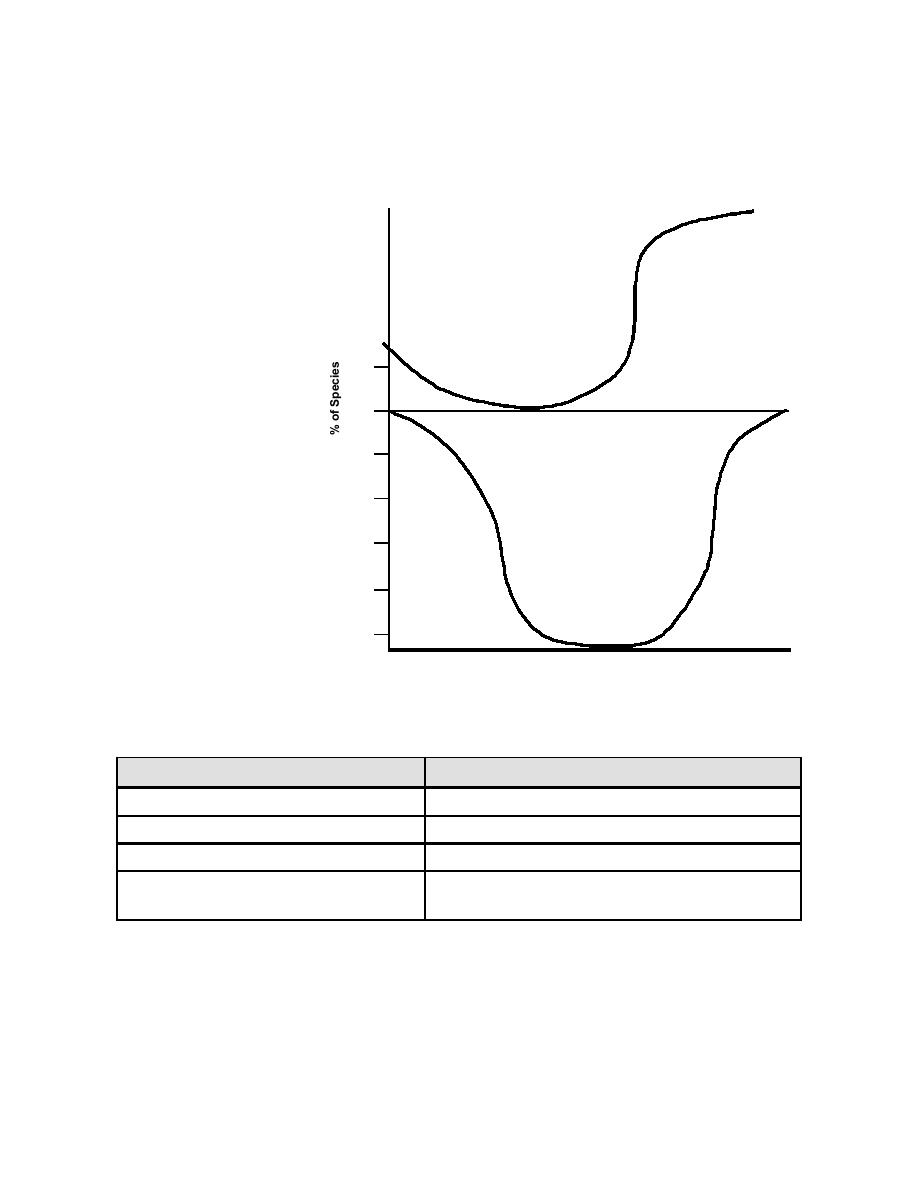
Figure 4-16. Halogen Species vs. pH in Water
80
hypochlorous acid
HOCl
=
OCl-
hypochlorite ion
=
hydrobromous acid
HOBr
=
60
hypobromite ion
Obr
=
Cl2
=
chlorine
bromine
Br2
=
40
-
OCl
HOCL
20
Cl2
0
HOBr
80
60
40
-
2
OBr
Br2
20
0
2
4
6
8
12 pH
10
Table 4-4. Chlorine Release Agents
Release Agents
Comments
Sodium hypochlorite 12%
Concentrated liquid bleach
Calcium hypochlorite (HTH)
Dry product; releases chlorine
Chlorine gas
Gaseous chlorine
Dry organic chlorine compound; releases
Chloroisocyanurates
chlorine and cyanuric acid
4-4.4.1.2
Bromine Release Agents. Bromine (Br2) compounds are very similar to
chlorine compounds. Although more expensive than chlorine compounds, their main
advantage is that bromine is more effective at higher pH ranges (7.5 or greater) than
chlorine. Bromine has a lower vapor pressure than chlorine and is 6 times as soluble in
water, making it less subject to vaporization loss from a cooling tower. When bromine is
introduced to water, it hydrolyzes to form hypobromite ion (OBr-) and hypobromous acid
(HOBr); Figure 4-16 shows this relationship. A pH range of 7.5 to 10.0 is considered
118



 Previous Page
Previous Page
