UFC 4-023-03
25 January 2005
7-3
ALTERNATE PATH METHOD FOR WOOD.
The Alternate Path approach is used to verify that the structure can bridge
over removed elements. The general procedure provided in Section 3-2 must be
followed.
7-3.1
Acceptability Criteria for Wood
The acceptability criteria are provided in Table 7-2; calculate the design
strengths per AF&PA/ASCE 16-95. The subsequent actions for the AP model after
violation of the acceptability criteria are detailed in the following sub-sections.
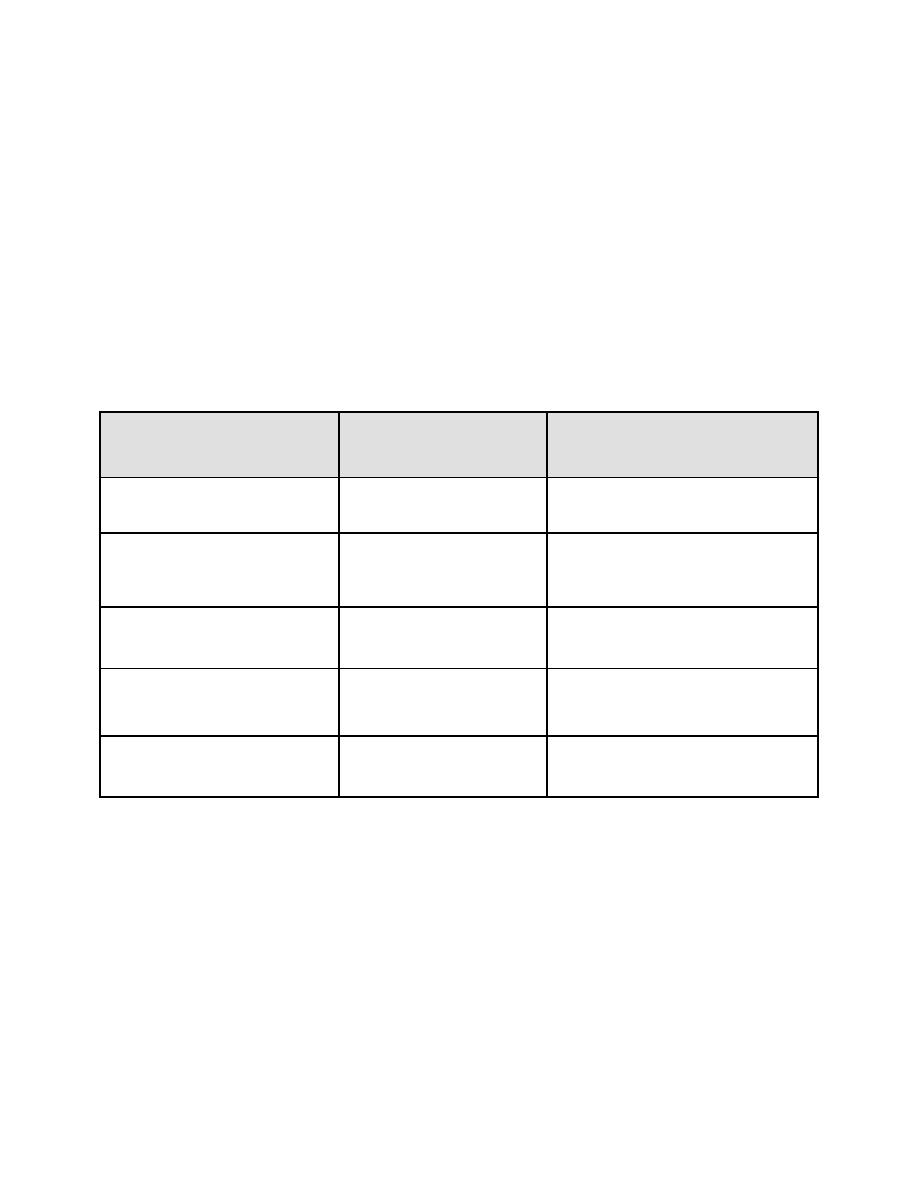
Table 7-2 Acceptability Criteria and Subsequent Action for Wood
Subsequent Action for AP
Structural Behavior
Acceptability Criteria
Model
Φ λ M'A
Element Flexure
Section 7-3.1.1
AF&PA/ASCE 16-95
Element Combined Axial
Chapter 6 Interaction
Section 7-3.1.2
and Bending
Equations, Include λΑ
Φ λ V'A
Element Shear
Section 7-3.1.3
Connection Design
Connections
Section 7-3.1.4
Strength, Include λΑ
Deformation Limits,
Deformation
Section 7-3.2
Defined in Table 7-3
A
Nominal strengths are calculated with the appropriate material properties and over-
strength factor Ω. All Φ factors are defined per AF&PA/ASCE 16-95. The over-
strength factor and time effect factor are both 1.0
7-3.1.1
Flexural Resistance of Wood.
For wood, the flexural design strength is equal to the nominal flexural
strength, calculated with the appropriate over-strength factor Ω and time effect factor λ,
multiplied by the strength reduction factor Φ. Calculate the nominal flexural strength per
Chapter 5 of AF&PA/ASCE 16-95. If the required moment exceeds the flexural design
strength, remove the element and redistribute the loads associated with the element per
Section 3-2.4.3.
7-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
