2.
ACCEPTABLE POWER SUPPLY.
a.
Primary. The primary source of power may be Navy-owned generating
equipment or one or more feeders from an outside electric power system.
Distribution voltages are generally 440/277 volts, 3-phase, 60 Hz, or 208/120
volts, 3-phase, 60 Hz AC.
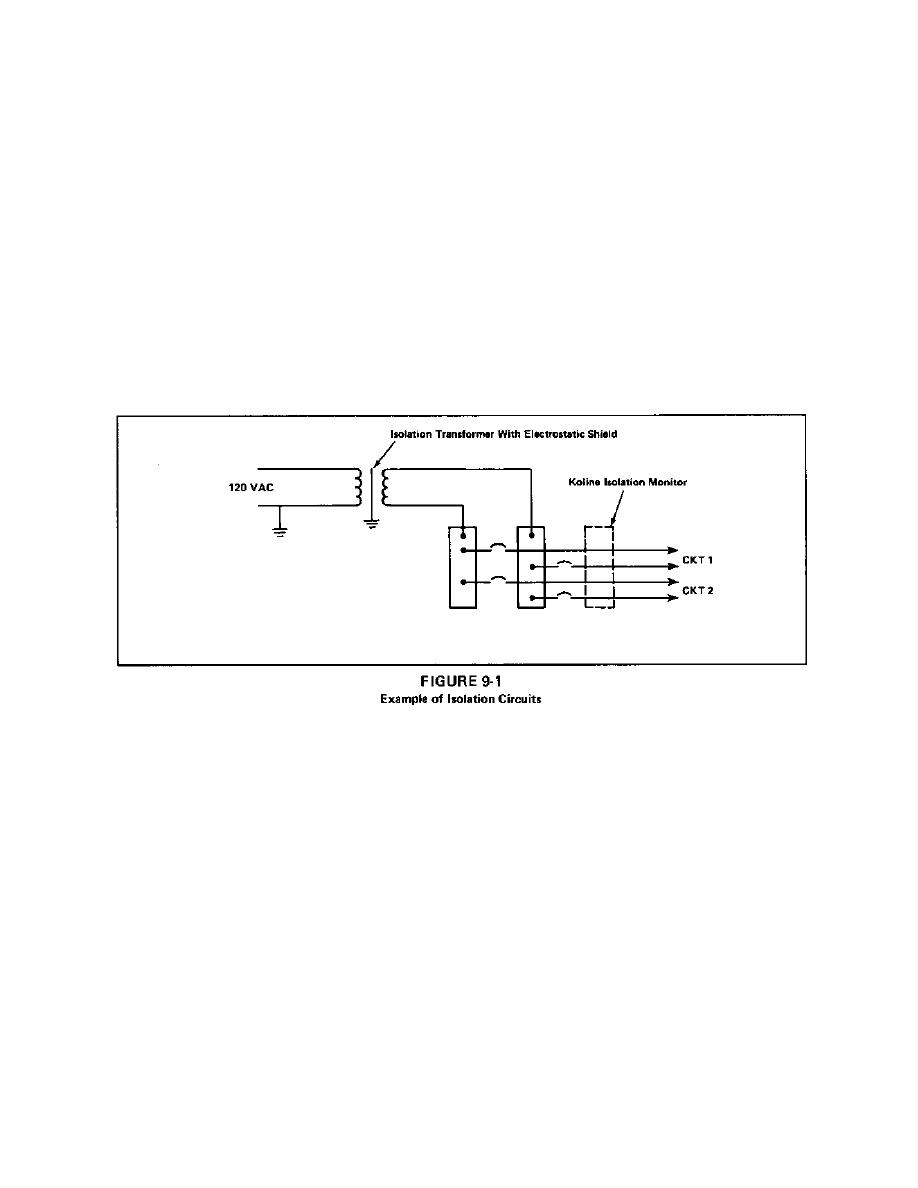
Potentials inside the chamber should not exceed 120 volts and should be
supplied from an ungrounded electrical system fed from isolation transformers
to minimize shock and fire hazards. See Figure 9-1. If power to devices in
the chamber is from a grounded source, ground fault protection must be
provided.
Consideration should be given to the use of low voltage dc power for
equipment in hyperbaric chambers.
b.
Standby. The standby source of power may be Navy-owned generation
or service supplied over a feeder or feeders from a different outside
electric power supplier. The most important requirement for a standby supply
is to insure that chamber life support, and basic monitoring and
communication functions are not interrupted for more than a minute by a
primary power failure. The simplest standby is an auxiliary gasoline or
diesel engine driven generator set to take over supply at the mains. The
auxiliary generator set should have battery start capability with automatic
initiation at the moment of failure of the primary supply. The generator set
should also have manually initiated electric start and hand cranking or hand
accumulator start for use if the automatic starting sequence fails. The
generator set battery supply should be accessible for checking and charging
at specified intervals. Simulated failures with automatic and manual
starting should be rehearsed at specified intervals. An additional battery
power supply should be maintained to provide power for monitoring critical
life support functions such as partial pressure oxygen and carbon dioxide
(PO2 and PCO2) and the fire protection system.



 Previous Page
Previous Page
