UFC 3-570-06
JANUARY 31 2003
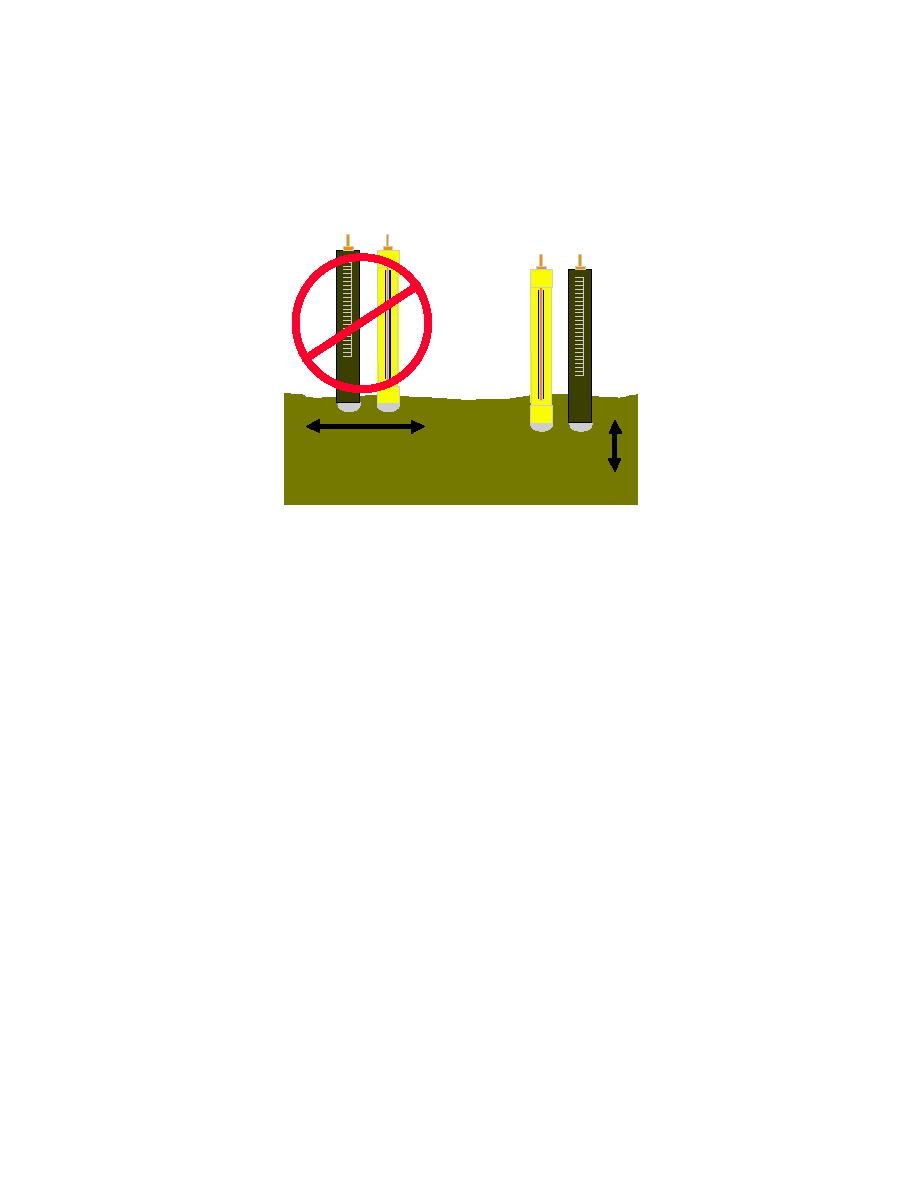
Figure 7-32. pH Measurement with Electrolyte Current Flow
IN CO RR E CT
R EC OM M E N DE D
C UR RE N T F L OW
C UR RE N T F L OW
E LE C TR OL Y TE
7-12.2
Chemical Test Method. Chemical test methods are usually associated with
liquid electrolyte samples. Chemical methods of measuring pH involve either the use of
pH measuring electrodes or indicators whose colors are dependent on pH. A pH meter
measures the difference in potential between a pH-insensitive reference electrode and an
electrode whose potential is sensitive to pH. Colored indicators are normally used in the
form of pH papers. The paper is wetted with the solution being measured and the
resulting color is compared with color standards to determine the pH. When chemical
meters or indicators are used to measure the pH of soil, the following procedure is used:
a small amount of soil is (one or two tablespoons) placed in a clean container and an
equal amount of water is added; after stirring, the mixture is allowed to settle and the pH
of the liquid is measured.
7-13
of cathodic protection test station that is vital for determination of the direction and
magnitude of DC current flowing through a pipeline. In protected pipelines, this
information can be used to verify current distribution, look for stray or interference
current, and the area of influence of installed rectifiers. In unprotected pipelines, this
information can be used to find anodic areas, and to find discharge or pickup areas of
stray or interference currents. This method uses the metallic pipeline or cable as a
shunt, which is then calibrated and used to measure a millivolt "IR Drop," from which the
current can be calculated. A known amount of DC current is applied to the pipeline and
the voltage drop across the length is measured (paragraph 7-13.1). The resistance can
be estimated if the size of the pipeline and distance of the test span is accurately known
(paragraph 7-13.3). The line current can be determined by the null ammeter method,
using a Multi-Combination meter (paragraph 7-13.4). One other method for determining
the direction and magnitude of DC current flowing through a pipeline is to use a clamp-
7-48



 Previous Page
Previous Page
