MIL-HDBK-1110
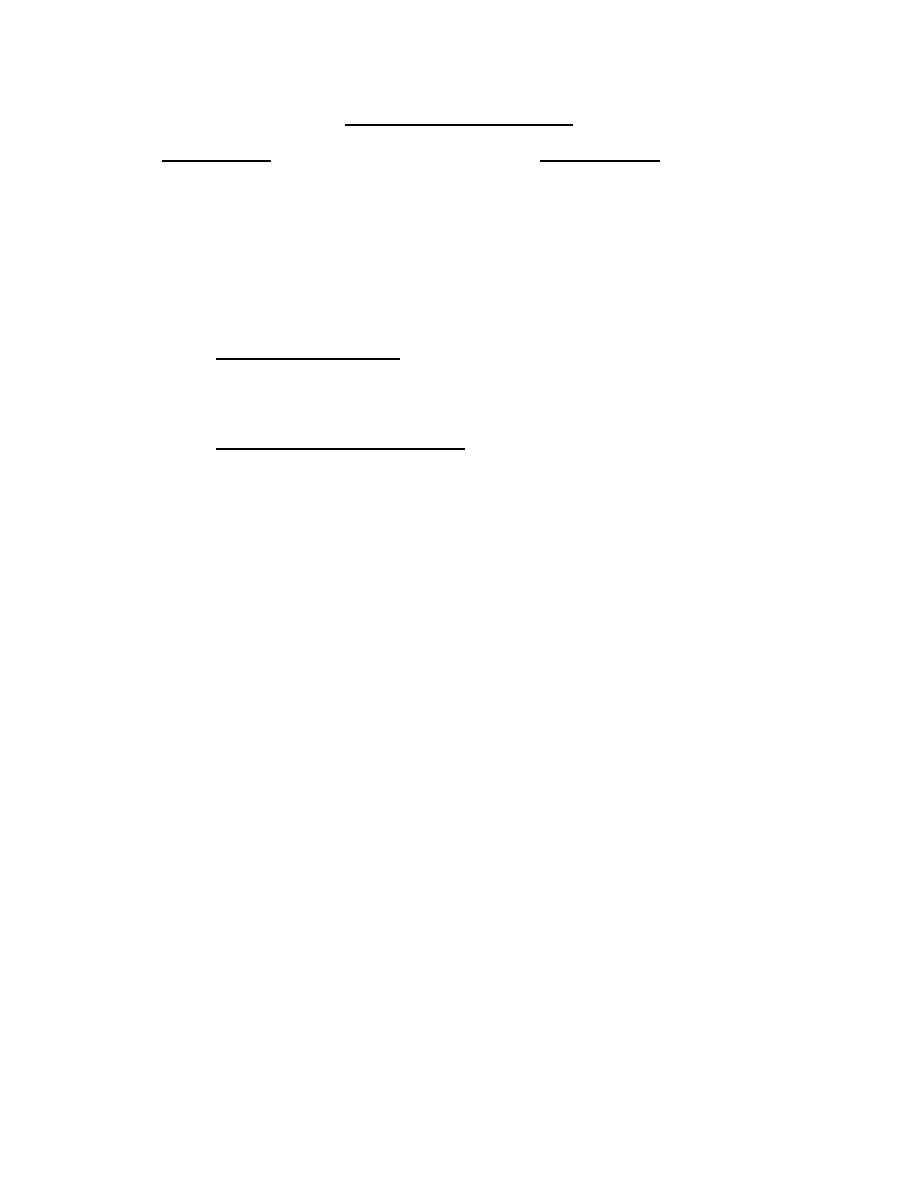
Polyurethane Coatings
Advantages
Limitations
Low in VOCs
Highly toxic; need personal
Good solvent resistance
protection
Good hardness or flexibility
Moisture sensitive; gloss may
May have excellent gloss
drop
Good durability
Skilled applicator needed
Good abrasion resistance
Limited pot life
Blasted surface required
High cost
2.3.7
Polyester Coating. Polyester coatings are used most
with fiberglass or glass flake reinforcement. They can be very
tough and durable but are seldom used today on military
facilities except with glass reinforcement.
2.3.8
Inorganic Zinc Coatings. Inorganic zinc coatings
usually have a silicate resin and may cure by several different
mechanisms. They can be formulated to be acceptably low in VOCs,
particularly the water-based products. The silicate film is very
hard and abrasion resistant. When applied too thickly, they may
mud crack. Thus, they are generally applied at less than 5 mils
dft, although some products can successfully be applied at
greater thicknesses. They provide cathodic protection to steel,
but as the zinc corrosion products fill the natural film
porosity, they begin to provide barrier protection. If this
barrier is broken by impact, cathodic protection will again take
over until the break is healed by again filling with zinc
corrosion products. They require greater steel surface
cleanliness than do other coating types. They must be applied by
a skilled applicator using a constantly agitated pot to keep the
heavy zinc particles suspended. Inorganic zinc silicate coatings
frequently do not bond well to each other, and it is safest to
repair them using a zinc-rich organic coating. Problems may
occur when topcoating them with organic coatings. Small bubbles
of air or solvent vapors escaping from the porous silicate film
may create holidays. Because of this concern, and their good
performances without topcoating in a variety of services, it is
often best not to topcoat them.
Zinc-rich organic coatings require less surface
preparation and are easier to topcoat than inorganic zinc
products. However, if properly applied, inorganic zinc coatings
are extremely durable in an atmospheric environment, the steel
preferentially receiving cathodic protection from the zinc. The
zinc is attacked, however, by acid and alkali (i.e., is
19



 Previous Page
Previous Page
